As our digital world continues to evolve, the demand for faster and more reliable internet connections is on the rise. This need for high-speed connectivity has led to significant advancements in the field of fiber-optic technology. Two key players in this arena are XG-PON (10G-PON) and GPON (Gigabit Passive Optical Network) ONUs (Optical Network Units). In this article, we’ll delve into the ONU vs GPON advancements and differences between these two technologies.
Understanding GPON
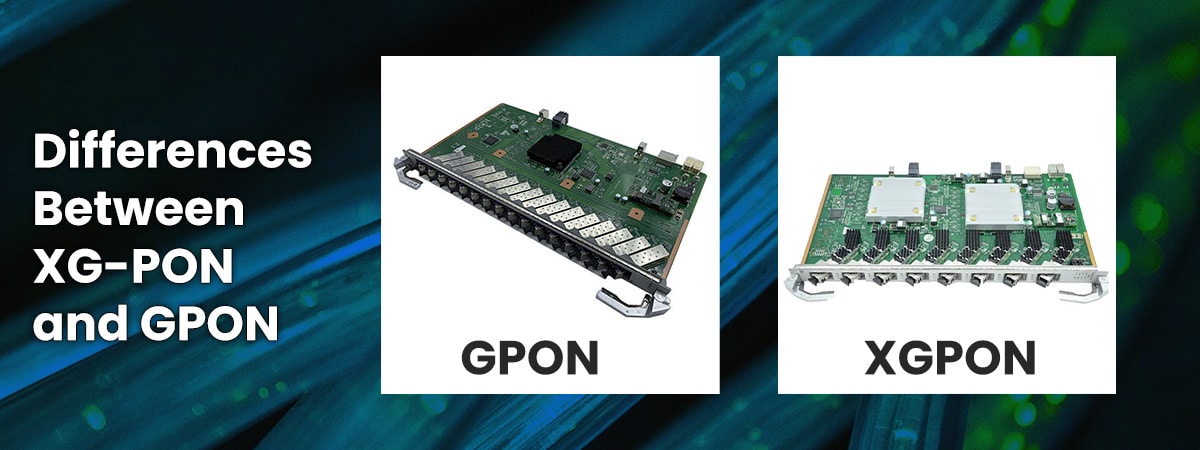
GPON, or Gigabit Passive Optical Network, has been a go-to solution for delivering high-speed internet access for some time now. It’s a point-to-multipoint access technology that uses passive optical splitters to share fiber-optic lines among multiple users. GPON is capable of delivering downstream speeds of up to 2.5 Gbps and upstream speeds of up to 1.25 Gbps.
The Emergence of XG-PON

XG-PON, or 10G-PON, represents the next level of fiber-optic technology. It’s designed to meet the growing demand for faster and more robust network connections. XG-PON offers impressive speeds, with downstream rates of up to 10 Gbps and upstream rates of up to 2.5 Gbps, making it an ideal solution for high-data-demand applications and services.
Advancements in XG-PON:
- Higher Speeds: The most noticeable advancement in XG-PON is its capability to deliver significantly higher speeds than GPON. With 10 Gbps downstream, it easily handles bandwidth-hungry applications and heavy data traffic.
- Low Latency: XG-PON boasts lower latency compared to GPON, making it suitable for real-time applications such as online gaming and video conferencing.
- Support for Emerging Technologies: XG-PON is well-prepared to support the demands of emerging technologies like 5G, IoT (Internet of Things), and 8K video streaming.
Differences Between XG-PON and GPON- ONU vs GPON
- Speed: The primary difference between XG-PON and GPON is the speed. XG-PON offers ten times the downstream speed of GPON.
- Latency: XG-PON typically has lower latency than GPON, which can be critical for real-time applications.
- Use Cases: XG-PON is better suited for high-data-demand environments and applications, while GPON is often sufficient for most residential and small business needs.

Choosing the Right Technology:
The choice between XG-PON and GPON depends on your specific needs. If you’re running a business with high-data-demand applications, require low-latency connections, or want to future-proof your network for emerging technologies, XG-PON is the way to go. For most residential and small business applications, GPON provides ample speed and reliability.
In conclusion, the advancements in fiber-optic technology are bridging the gap between the demand for faster internet connections and what is technologically feasible. While GPON continues to serve many users well, XG-PON is pushing the boundaries of what’s possible with its impressive speed and low latency, making it the technology of choice for advanced applications and high-data-demand environments.
Call to Action:
If you’re considering upgrading your network to XG-PON or GPON technology or need expert guidance on the right choice for your specific needs, don’t hesitate to reach out to us. Our team is here to help you make an informed decision and optimize your network for the future.
Explore More:
A Comprehensive Comparison of ZTE F670L, EG8145V5, and HS8546X6 ONUs
FTTO vs. FTTH: The Role of XG-PON ONT