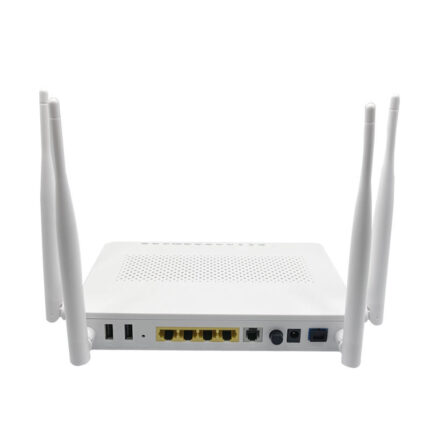
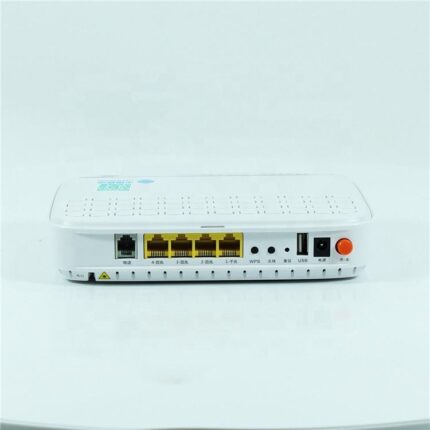
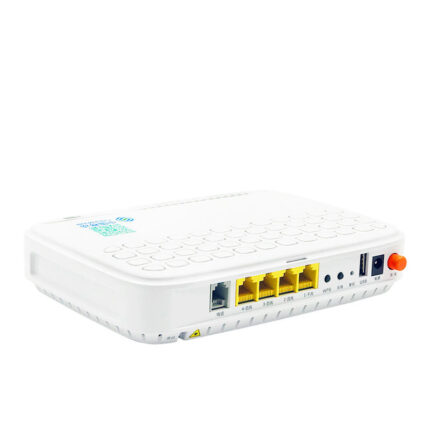
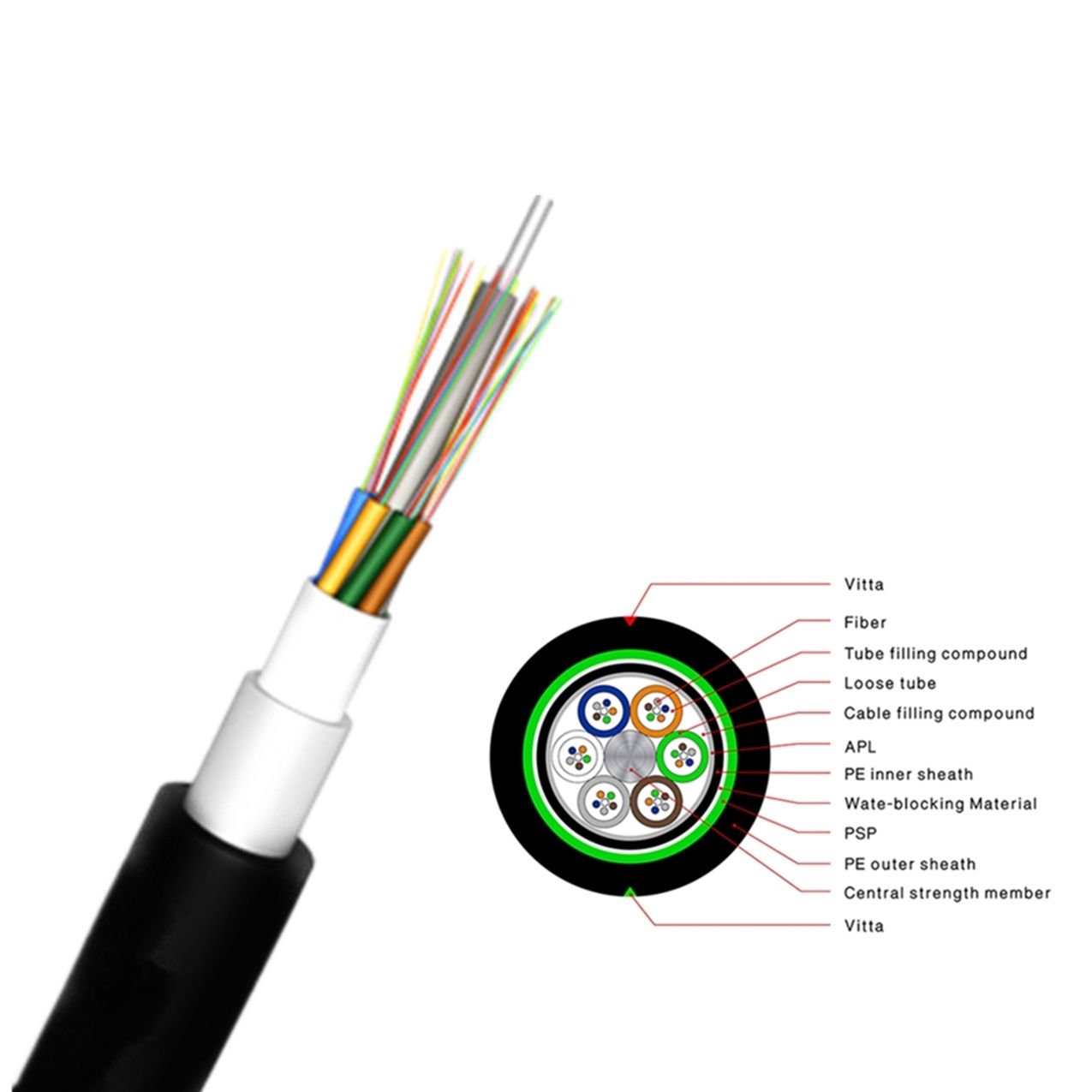
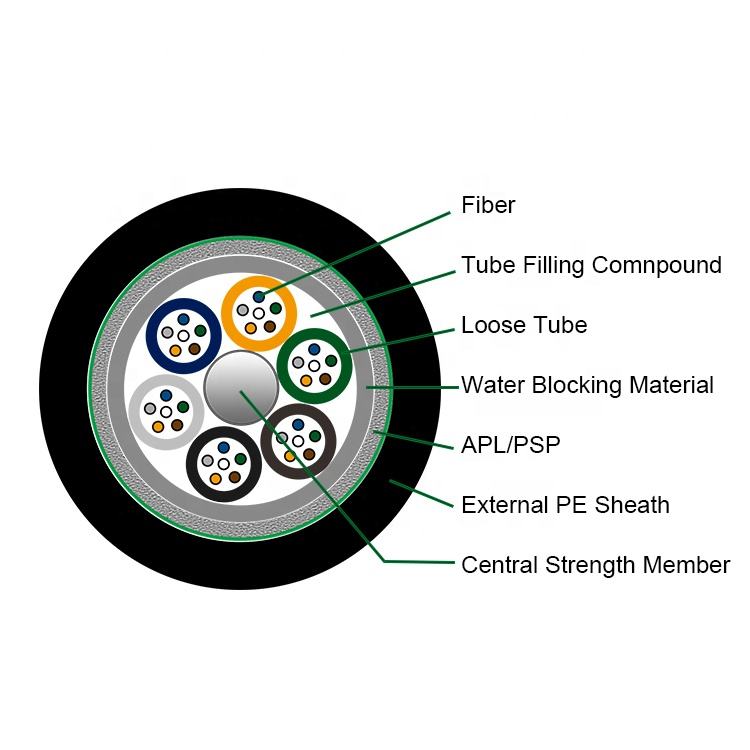
ADSS Fiber Optic Cable Description:
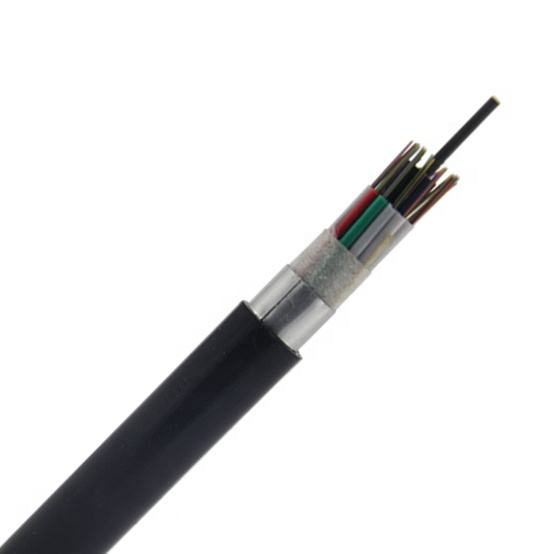
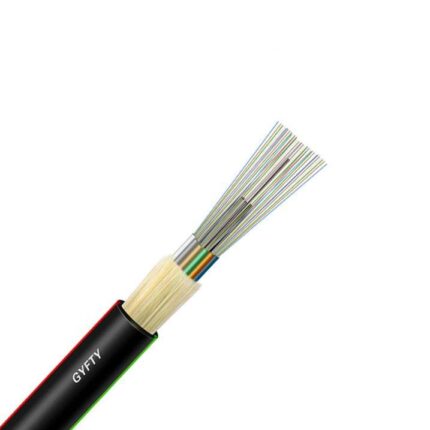
ADSS cable adopts loose tube gysts structure, optical fiber into the pine casing made of high modulus polyester material, waterproof casing filling compound pine casing (and filling line) around non-metallic center (FRP) to strengthen core twisted into a compact core, core within the gap filled with gel core outer extrusion polyethylene (PE) inner sheath, and then strengthen the bidirectional twisted around two layers of the function of aramid yarn, finally extrusion polyethylene (PE) coat or electrical erosion resistance (AT) your coat.
Characteristics:
· Good mechanical and temperature performance
·High strength loose tube that is hydrolysis resistant
·Special tube filling compound ensure a critical protection of fiber
·Crush resistance and flexibility
·The following measures are taken to ensure the cable watertight:
-Single Fiber Reinforced Plastic as the central strength member
-Loose tube filling compound
-100% cable core filling
-PSP enhancing moisture-proof
-Water-blocking material
Applications:
ADSS (All-Dielectric Self-Supporting) fiber optic cables are specifically designed for aerial installations, where they are deployed without the need for additional support structures like messenger wires. Here are some common applications of cables:
- Telecommunications Networks: ADSS cables are extensively used in telecommunications networks for long-distance communication links between buildings, telephone exchanges, cell towers, and other network nodes. Their self-supporting design makes them ideal for spanning across utility poles and minimizing installation time and costs.
- Internet Service Providers (ISPs): ISPs often deploy ADSS cables to expand their network infrastructure and provide high-speed internet access to residential and commercial customers. These cables facilitate the transmission of broadband data over long distances, supporting services such as fiber-to-the-home (FTTH), cable internet, and digital subscriber line (DSL).
- Electric Utility Networks: ADSS cables are commonly deployed in electric utility networks for communication and monitoring purposes. They enable utilities to establish reliable communication links for supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA), smart grid applications, distribution automation, and remote metering.
- Transportation Infrastructure: ADSS cables are used in transportation infrastructure projects such as railways, highways, and airports to establish communication networks for traffic management, surveillance, and passenger information systems. They provide high-bandwidth connectivity for cameras, sensors, and control systems deployed along transportation routes.
- Oil and Gas Industry: In the oil and gas industry, ADSS cables are employed for communication and data transmission in remote oil fields, pipelines, and drilling operations. They support applications such as remote monitoring of equipment, control of pumping stations, and real-time data acquisition for production optimization and safety.
- Government and Defense: ADSS cables are utilized by government agencies and defense organizations for establishing secure communication links in strategic locations, military bases, and border surveillance systems. Their robust construction and resistance to environmental factors make them suitable for mission-critical applications in challenging terrains.
- Educational and Research Institutions: Educational institutions and research facilities deploy ADSS cables to create high-speed networks for scientific research, data transfer, and collaboration among researchers. These cables support the transmission of large datasets, video conferencing, and remote access to scientific instruments and resources.
Features:
ADSS (All-Dielectric Self-Supporting) fiber optic cables are designed for aerial installation where traditional metallic or hybrid cables might be unsuitable or more challenging to deploy. Here are some of their key features:
- Dielectric Construction: ADSS cables are constructed entirely of dielectric materials, meaning they contain no metallic components. This design eliminates the risk of electrical conductivity, making them suitable for use in high-voltage environments like power lines.
- Self-Supporting: ADSS cables are designed to support their weight along spans between support structures (such as utility poles) without the need for a separate messenger wire or other support elements. This self-supporting feature simplifies installation and reduces deployment costs.
- High Tensile Strength: Despite their lightweight construction, ADSS cables are engineered to withstand the tension forces experienced during installation and service. They typically use aramid yarns or fiberglass rods as strength members to provide robust mechanical performance.
- Weatherproofing: ADSS cables are designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions, including extreme temperatures, UV radiation, moisture, and wind. They are often jacketed with materials such as polyethylene (PE) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC) to provide protection against weathering.
- Low Sag: ADSS cables are designed to maintain low sag under various environmental conditions, ensuring that they remain clear of obstacles and maintain proper clearance from the ground or other structures.
- Fiber Count and Configuration: ADSS cables are available with various fiber counts and configurations to suit different bandwidth requirements and network architectures. They can accommodate both single-mode and multimode fibers.
- Long Spans: ADSS cables are suitable for long-distance aerial installations, where spans between support structures can extend for hundreds of meters or more. This capability makes them ideal for use in rural areas or across challenging terrain.