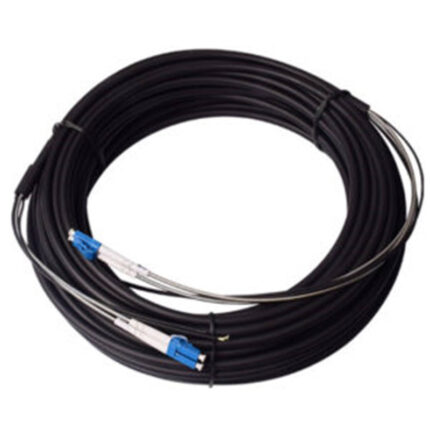
drop fiber optic cable Overview:
The term “drop fiber optic cable” typically refers to a specific type of cable used in fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) or fiber-to-the-premises (FTTP) installations. Here’s a description of drop fiber optic cables:
- Design: Drop fiber optic cables are designed for the final link in the fiber optic network, connecting the main distribution network to individual homes, businesses, or buildings. They are often lightweight and flexible, making them easy to handle and install in various environments.
- Construction: These cables typically consist of one or more optical fibers enclosed in a protective jacket. The jacket material is chosen to provide durability and resistance to environmental factors such as UV radiation, moisture, and temperature fluctuations.
- Strength Member: Some drop cables may include a strength member, such as aramid yarns (e.g., Kevlar), to provide additional tensile strength and protect the fibers from stretching or damage during installation.
- Connectorization: Drop cables may come pre-connectorized with connectors such as SC, LC, or ST at one or both ends. This facilitates quick and easy installation, as the connectors can be plugged directly into optical network terminals (ONTs) or other termination points without the need for splicing.
- Installation: Drop fiber optic cables are typically installed aerially, buried underground, or run along building exteriors to reach the subscriber’s premises. They may be deployed using various installation methods, including overhead suspension, direct burial, or conduit placement, depending on local regulations and environmental conditions.
- Bend Radius: Drop cables are often designed to have a small bending radius, allowing them to navigate tight corners and bends without signal loss or damage to the fibers. This flexibility is crucial for routing the cable through conduits, around corners, and into tight spaces during installation.
- Performance: Drop fiber optic cables are engineered to meet industry standards for optical performance, including low attenuation, high bandwidth, and low signal loss. They ensure reliable transmission of high-speed data, voice, and video signals from the service provider’s network to the subscriber’s premises.
Applications:
Drop fiber optic cables serve various applications primarily focused on extending high-speed internet access and advanced communication services to individual users and premises. Here are some common applications:
- Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH): Drop fiber optic cables are extensively used in FTTH deployments, where they connect the optical network terminal (ONT) installed inside a subscriber’s home or building to the service provider’s fiber optic network. They enable the delivery of ultra-fast broadband internet, digital television, voice over IP (VoIP), and other multimedia services directly to residential users.
- Fiber-to-the-Business (FTTB): In FTTB installations, drop fiber optic cables connect commercial buildings, offices, and businesses to the service provider’s fiber optic infrastructure. They support high-speed internet access, cloud computing, video conferencing, and other business-critical applications, enhancing productivity and efficiency in corporate environments.
- Multi-Dwelling Units (MDUs): Drop fiber optic cables are deployed in apartment buildings, condominiums, and gated communities to provide fiber optic connectivity to multiple residential units within the same building or complex. They enable residents to access high-speed internet, digital TV, and other broadband services independently, enhancing quality of life and property value.
- Remote Areas and Rural Communities: Drop fiber optic cables are used to bridge the digital divide and extend broadband access to remote areas and underserved rural communities. They enable residents in rural regions to access high-speed internet, telemedicine, distance learning, and e-commerce services, unlocking economic opportunities and improving quality of life.
- Educational Institutions: Drop fiber optic cables are deployed in schools, colleges, and universities to provide high-speed internet access and networking infrastructure for students, faculty, and staff. They support online learning, research activities, digital libraries, and collaborative projects, enriching educational experiences and promoting knowledge sharing.
- Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs): Drop fiber optic cables are utilized by small and medium-sized businesses to establish reliable and scalable communication networks. They enable SMEs to access cloud-based applications, hosted services, virtual private networks (VPNs), and unified communications platforms, enhancing connectivity and competitiveness in the marketplace.
- Smart Homes and Internet of Things (IoT): In smart home and IoT applications, drop fiber optic cables support the connectivity of smart devices, sensors, and appliances within residential environments. They enable homeowners to automate and control lighting, security, heating, and other systems remotely, improving energy efficiency, convenience, and security.
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| Cable Type | Drop fiber optic cable |
| Fiber Count | Typically 1 to 4 fibers (can vary based on requirements) |
| Fiber Type | Single-mode (SM) or multimode (MM) |
| Fiber Diameter | Single-mode: 9/125 µm, Multimode: 50/125 µm or 62.5/125 µm |
| Jacket Material | Polyethylene (PE), Low Smoke Zero Halogen (LSZH), or other suitable material |
| Strength Member | Aramid yarns (e.g., Kevlar) or fiberglass reinforced plastic (FRP) |
| Connector Type | SC, LC, or other standard connector types |
| Cable Length | Customizable based on installation requirements |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +70°C |
| Installation Temperature | -20°C to +60°C |
| Bending Radius (Install) | ≥ 10 x Cable Diameter |
| Bending Radius (Operation) | ≥ 5 x Cable Diameter |
| Crush Resistance | ≥ 1000 N/100 mm |
| Tensile Strength | ≥ 500 N (short-term), ≥ 200 N (long-term) |
| Standards | Compliant with relevant industry standards (e.g., ITU-T, ANSI/TIA) |
| Applications | Fiber-to-the-home (FTTH), Fiber-to-the-business (FTTB), MDUs, Rural Connectivity, Smart Homes, IoT, etc. |
For more: Click here