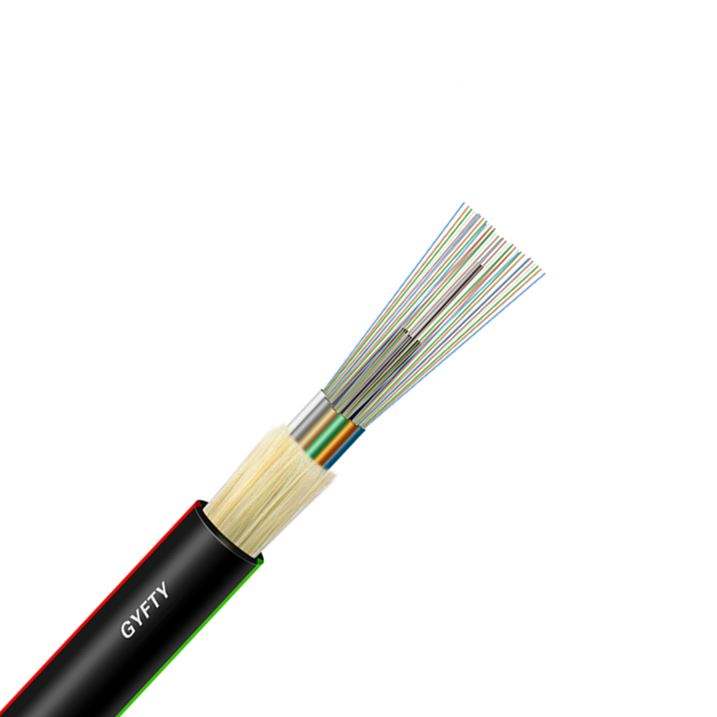
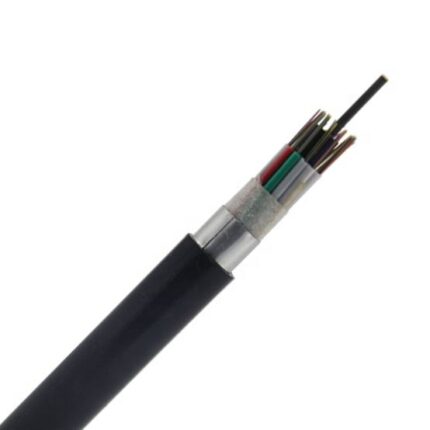
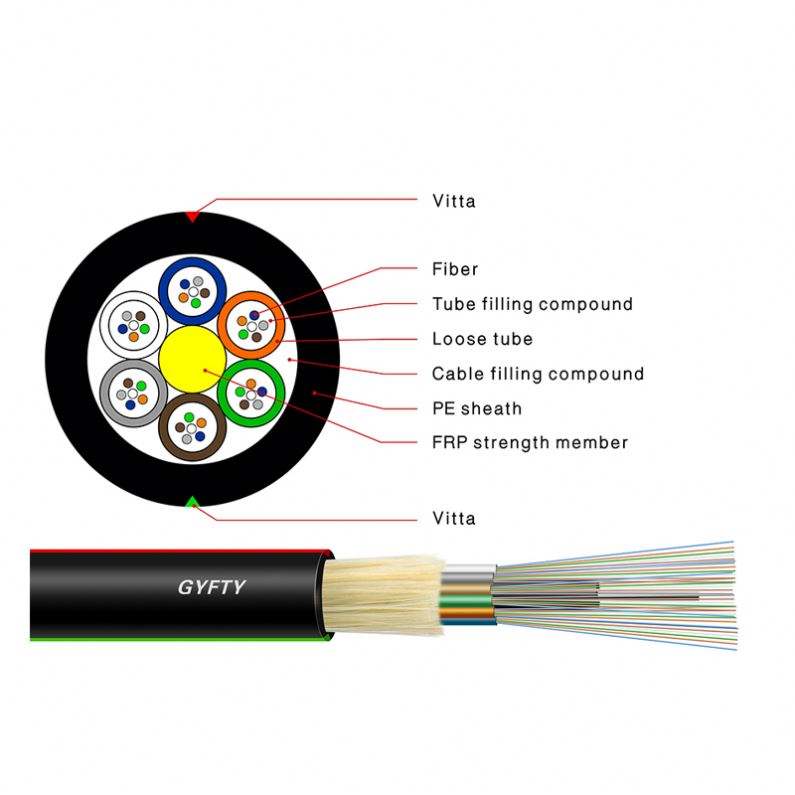
GYFTY 63 Overview:
GYFTY 63 the fibers are positioned into a loose tube made of high modulus plastics. Filled with a water-blocking filling compound, the tube is stranded around FRP as a non-metallic central strength member into compact and circular cable core. Then covered with thin PE (polyethylene) inner sheath and a layer of aramid yarn, the cable is completed with a PE outer sheath. ADSS cables are ideal for outside plant aerial applications, the lightweight cable and all-dielectric construction allow cost-effective and safe installation in high voltage overhead power lines.
GYFTY 63 Features:
* High strength loose tube that is hydrolysis resistant
* Special tube filling compound ensure a critical protection of fiber
* Crush resistance and flexibility
* The following measures are taken to ensure the cable watertight:
* Single Fiber Reinforced Plastic as the central strength member
* Loose tube filling compound
* 100% cable core filling
* PSP enhancing moisture-proof
* Water-blocking material
Applications:
- Direct Burial: This application involves the installation of cables or pipelines directly into the ground without the use of any protective conduits or channels. It’s commonly employed in scenarios where the terrain allows for straightforward burial, such as rural areas or private properties. Direct burial offers a cost-effective and efficient means of laying cables for utilities like electricity, telecommunications, or plumbing.
- Underground: In this application, cables or pipelines are laid beneath the surface of the ground within protective conduits or trenches. Unlike direct burial, underground installations often require additional measures for protection against environmental factors, such as moisture, temperature variations, and physical damage. This method is frequently used in urban environments, highways, or areas with high pedestrian or vehicular traffic where durability and longevity are essential.
- Backbone Internet: The backbone internet application involves the deployment of high-capacity fiber optic cables or other networking infrastructure to form the core of the internet’s communication network. These backbone networks connect major network access points, data centers, and internet exchange points, facilitating the transmission of vast amounts of data across long distances at high speeds. Backbone internet infrastructure plays a critical role in supporting the global connectivity and functionality of the internet, enabling services like cloud computing, online streaming, and real-time communication.
Characteristics:
1.Excellent mechanical and temperature performance
2.Special tube filling compound ensure a critical protection of fibre and resist the water
3.100% core filling water prevent cable jelly to ensure the cable watertight
4.Single FRP as the central strength member to withstand axial loads
5.Outer sheath protects cable from ultraviolet radiation
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| Cable Type | GYFTY (Non-metallic, Aerial/Duct) |
| Fiber Count | 24 cores |
| Fiber Type | Single-mode (SM) or Multi-mode (MM) |
| Fiber Diameter | Typically 9/125 μm (SM) or 50/125 μm (MM) |
| Cable Diameter | 12.0 – 15.0 mm (depending on design) |
| Jacket Material | Polyethylene (PE) |
| Strength Member | Dielectric (FRP or steel) |
| Installation Method | Outdoor (Aerial or Duct) |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +70°C |
| Tensile Strength | Typically 1500 – 3000 N |
| Crush Resistance | Typically 1000 – 3000 N/100mm |
| Bending Radius | Static: 10x cable diameter |
| Dynamic: 20x cable diameter | |
| UV Resistance | Yes (for outdoor applications) |
| Water Resistance | Yes (for outdoor applications) |
| Application | Long-distance communication, backbone networks, outdoor installations |
| Compliance | ITU-T G.652.D, IEC 60794, RoHS |
For more: Click here